Airborne particles are a major cause of respiratory ailments of humans, causing allergies, asthma, and pathogenic infections of the respiratory tract. Airborne fungal spores are also important agents of plant disease, and the means for dissemination of many common saprotrophic (saprophytic) fungi. Its is an important respiratory diseases of humans,the roles of airborne spores in crop diseases and the methods used to monitor spore populations in the air.
The surfaces of the human body inside and out, for sample the skin, mouth and the intestines, are covered in millions of individual micro-organisms that don’t do us any harm. In fact they help to protect us from becoming infected with harmful microbes. They are known as the normal body flora.
The number of normal bacterial cells that live on the body is in the region of 100 million. This number is 10 times greater than the 10 million cells that make up the human body.
The resident flora at each site includes several different types of microorganisms. Some sites are normally colonized by several hundred different types of microorganisms. Environmental factors—such as diet, sanitary conditions, air pollution, and hygienic habits—influence what species make up a person's resident flora. If transiently disturbed (for example, by washing or use of antibiotics), the resident flora usually promptly reestablishes itself.
Rather than causing disease, the resident flora often protects the body against disease-causing organisms. However, under certain conditions, microorganisms that are part of a person's resident flora may cause disease. Such conditions include the use of antibiotics and a weakened immune system (as occurs in people with AIDS or cancer, people taking corticosteroids, and those receiving chemotherapy). When antibiotics used to treat an infection kill a large proportion of certain types of bacteria of the resident flora, other resident bacteria or fungi can grow unchecked. For example, if women take antibiotics for a bladder infection, the antibiotics kill some of the resident flora, allowing yeast in the vagina to multiply and cause a vaginal yeast infection.
Objective :
To determine the microorganisms in the air and healthy humans.
Materials and Reagent :
Molten nutrient agar
sterile water
Sterile petri dish
Sterile clinical swab
Pipette and tips
Procedure :
(refer to lab manual)
Results and Observations:
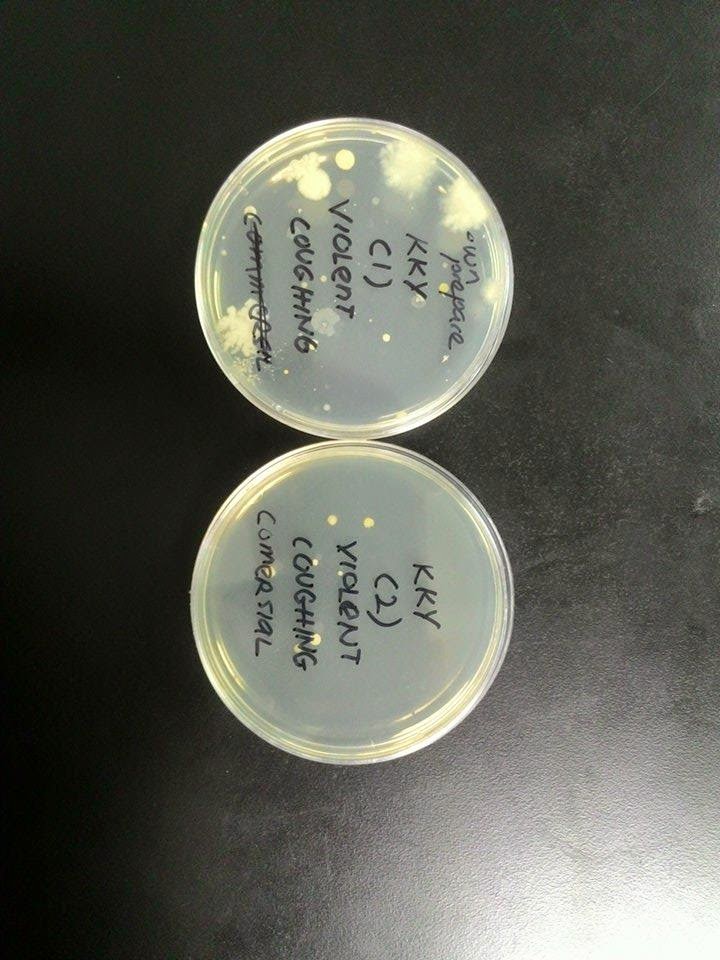
violent coughing:
hands:
Ear:
Normal Breathing:
Discussion:
scientist use colony morphology method todescribe the characteristics of an individual colony of bacteria growing on agar in a Petri dish. It can be used to help to identify them.
Different types of bacteria will produce different-looking colonies, some colonies may be coloured, some colonies are circular in shape, and others are irregular. A specific terminol
ogy is used to describe common colony types. For example is the basic shape of the colony,the diameter, the elevation,margin,surface,opacity and the colour of the bacteria.
violent coughing :
A cough is a sudden and often repetitively occurring reflex which helps to clear the large breathing passages from secretions, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. Actually the microbes during breathing and coughing are quite similar because there are originated from the same place, mouth and nose cavity in human beings.
normal breathing:
Our mouth contains a lot of pathogenic and non-pathogenic microorganisms. The pathogenic bacteria will cause some microbial diseases of the respiratory system which may occur in the upper or lower regions. Some examples of these non-pathogenic bacteria are Streptococcus, Neisseria, Haemophilus, and Micrococcus. Whereas the pathogenic bacteria might cause strep throat, scarlet fever, diptheria. The pathogenic bacteria are Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Streptococcus pyogenes,Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae.
ear:
Our mouth contains a lot of pathogenic and non-pathogenic microorganisms. The pathogenic bacteria will cause some microbial diseases of the respiratory system which may occur in the upper or lower regions. Some examples of these non-pathogenic bacteria are Streptococcus, Neisseria, Haemophilus, and Micrococcus. Whereas the pathogenic bacteria might cause strep throat, scarlet fever, diptheria. The pathogenic bacteria are Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Streptococcus pyogenes,Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Hand:
The hands and fingernails are often affected by fungal and yeast infections. Some of the species are Cladosporium, Scopulariopsis, Aspergillus, Acremonium, Epidermophyton,and Trichophyton. There are also some bacteria that exist on our hands. These are the few common examples, Serratia, Aeromonas, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus, Acinetobacter and Enterobacter.
air:
The atmosphere is not a very welcoming environment for many microorganisms. The joint effects of desiccation and sunlight cause many microbial cells to die rapidly when suspended in air. This is especially true of Gram-negative bacteria, including food borne pathogens like E. coli and Salmonella. Nevertheless, some Gram-positive bacteria and fungal spores can survive for long periods in the atmosphere and can be widely dispersed by air currents. The typical microflora of the air is usually made up of pigmented Gram-positive bacteria and bacterial and fungal spores, which are resistant to the drying effects of the air and to radiation. Unfortunately, it can include some pathogenic bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus, and common food spoilage fungi, notably species ofPenicillium and Aspergillus.
Conclusion:
From this experiment, we can conclude that our body consist of so many bacteria. Every single part of our body have billion type of bacteria, either harmful or not harmful. this bacteria will survive if the surface is suitable for their morphology.
Reference :
http://ibg102.wordpress.com/2013/05/02/lab-4-sources-of-contamination-and-infection/







No comments:
Post a Comment